Immunization billing plays a crucial role in healthcare today. Proper coding i.e. using CPT Code 90471 ensures providers get reimbursed for their services. It also helps maintain accurate patient records.
Yet, many practices struggle with vaccine billing errors. These mistakes can lead to significant revenue loss.
Enter CPT Code 90471, the central billing code for vaccine administration. This code helps healthcare providers bill for immunization services correctly.
Unfortunately, many providers still face high denial rates when using this code.
Why?
Because even small mistakes in coding can trigger rejections.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about CPT Code 90471. We’ll cover proper usage, documentation requirements, and billing best practices.
This information will help you improve your immunization reimbursement rates and reduce claim denials.
What is CPT Code 90471?
According to the AMA, CPT 90471 represents the “Immunization administration for one vaccine or toxoid component.”
What does it cover?
This code specifically covers the administration of an initial injectable vaccine.
It’s important to note that this code only covers the service of administering the vaccine. It does not include the vaccine product itself.
According to AFP, this code is for the administration of a vaccine or toxoid by intramuscular route in a patient 18 years of age or older, without counseling.
Additionally, the AMA maintains all CPT codes, including 9 0471.
These codes provide a standardized language for reporting medical services.
When you use CPT 90471, you’re telling payers that you provided immunization administration services.
- Procedure: Administration of a vaccine by intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intradermal injection
- Scope: Applies to one vaccine given during a patient visit
- Counseling: Can be used with or without counseling
- Settings: Commonly used in clinics, hospitals, urgent care centers, and physician offices
Administration Vs Product Code
Many providers confuse the administration code with the vaccine product code.
This confusion can lead to billing errors. Remember that CPT 90471 only covers the act of giving the injection.
You must separately bill for the actual vaccine using a product code.
This distinction is crucial for proper immunization administration and CPT billing.
Key Features of CPT 90471
CPT Code 90471 has several important features that providers should understand.
- First, this code covers all injectable routes. This includes intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, and percutaneous injections. You don’t need different codes based on how you deliver the vaccine.
- Second, CPT 90471 works for patients of all ages. You can use this code for both pediatric and adult patients. This makes it a versatile option for pediatric practices and family medicine offices alike.
- Third, this code applies only to the initial vaccine of a visit. If a patient receives multiple vaccines, you’ll need additional codes. This feature often confuses vaccine injection billing. Understanding this limitation is key to avoiding claim denials.
When to Use CPT 90471
You should use CPT 90471 when administering any initial injectable vaccine.
Common scenarios include flu shots, tetanus boosters, hepatitis vaccines, pneumonia vaccines, and rabies vaccines. For a flu shot billing code, 90471 is typically your go-to option.
Pediatric practices frequently use this code during annual wellness visits.
When children receive their routine immunizations, CPT 90471 helps bill for the administration service. Urgent care centers also rely on this code when providing tetanus vaccines or other immunizations.
Travel clinics represent another setting where this code proves valuable.
These clinics often administer various vaccines to travelers.
Each initial injectable vaccine would use CPT 90471 for proper hepatitis A immunization billing or other travel-related vaccines.
When NOT to Use CPT 90471
Understanding when not to use CPT 90471 is just as important as knowing when to use it.
- If a patient receives additional vaccines during the same visit, you should use code 90472 instead.
- This distinction between CPT 90471 vs 90472 CPT Code is a common source of vaccine billing mistakes.
- Never use 90471 for oral or nasal vaccines. These administration methods require code 90473. Using the wrong code here will likely result in claim rejection.
- Some payers bundle immunization administration into preventive visits.
In these cases, you shouldn’t bill separately for CPT 90471.
Check with each payer to understand their bundling policies. This vaccine CPT exclusion can save you from unnecessary denials.
CPT 90471 vs Related Codes
Usually, the healthcare providers become confuse and mix up the CPT 90471 with other relevant codes.
So, to avoid billing flaws and claims rejections, it is essential to keep other codes along with their conditions and procedures.
Additionally, physicians should also differentiate it from others.
Let’s compare CPT 90471 with related codes to clarify their proper usage.
| Code | Description | Key Difference |
| 90471 | Immunization administration for one vaccine/toxoid (initial) | For the first injectable vaccine of a visit |
| 90472 | Immunization administration for each additional vaccine/toxoid | For each subsequent injectable vaccine in the same visit |
| 90473 | Immunization administration by oral or nasal route | For non-injectable vaccines |
| 90715/90686 | Vaccine product codes | Represent the actual vaccine, not its administration |
This immunization CPT Code comparison shows that administration codes (90471-90473) differ from product codes (90715/90686).
You’ll often need to bill both an administration code and a product code for complete reimbursement. The difference between CPT 90471 vs 90472 is particularly important to master.
ICD-10 Codes for CPT Code 90471
Proper ICD-10 coding is essential when billing CPT 90471.
The primary diagnosis code for immunization administration is Z23. This code represents “Encounter for Immunization.” Most payers require this code when billing vaccine administration services.
However, certain situations may require additional ICD-10 codes:
| ICD-10 Code | Description | When to Use |
| Z23 | Encounter for Immunization | For routine immunizations |
| W49.0XXA | Contact with sharp object | For tetanus vaccine after injury |
| Z20.3 | Contact with and suspected exposure to rabies | For rabies vaccine after exposure |
| Z20.828 | Contact with and suspected exposure to other viral communicable diseases | For hepatitis vaccine after exposure |
Using the correct ICD-10 code for immunization is crucial. The Z23 CPT 90471 pairing is standard for most preventive vaccines. For rabies vaccine billing, ICD-10 codes like Z20.3 or W54.0XXA might be more appropriate depending on the situation.
Modifiers with CPT Code 90471
Modifiers can significantly impact how payers process your CPT 90471 claims.
With CPT 9071, usually two modifiers are used:
- Modifier 25
- Modifier 59
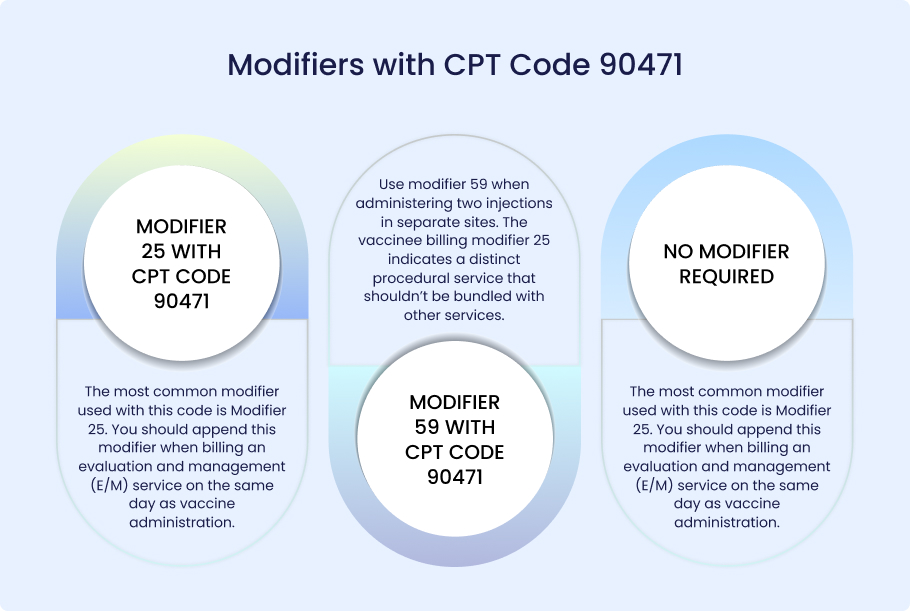
Modifier 25 with CPT Code 90471
The most common modifier used with this code is Modifier 25. You should append this modifier when billing an evaluation and management (E/M) service on the same day as vaccine administration. This tells the payer that the E/M service was a separate, significant service.
Modifier 59 with CPT Code 90471
Modifier 59 is another important modifier for vaccine billing. Use this modifier when administering two injections in separate sites. The vaccinee billing modifier 25 indicates a distinct procedural service that shouldn’t be bundled with other services.
No Modifier Required
However, don’t overuse modifiers with CPT 90471. Some providers incorrectly add modifiers to every claim. This practice can trigger audits. Only use modifiers when they accurately reflect the services provided. Understanding vaccine billing modifier 25 rules is essential for proper CPT Code 90471 reimbursement.
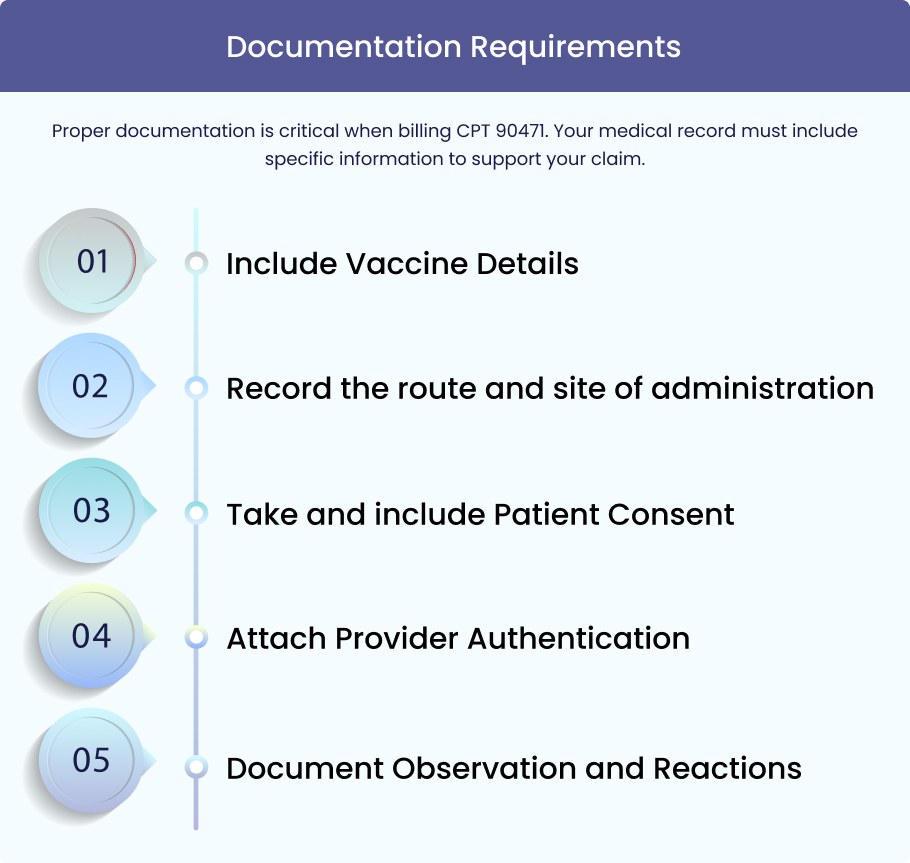
Documentation Requirements
Include Vaccine Details
First, document vaccine details including manufacturer, lot number, and expiration date. This information proves you administered a legitimate vaccine product.
Record the route and site of administration
Second, record the route and site of administration. Note whether the injection was intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous (SC), or another method.
Also, document the specific location, such as “left deltoid.” This level of detail supports your vaccine injection billing.
Take and include Patient Consent
Third, include patient consent documentation. This shows the patient agreed to receive the vaccine.
Attach Provider Authentication
Fourth, ensure provider authentication through a signature or e-signature. This verifies who performed the service.
Document Observation and Reactions
Finally, document any observation period and note any adverse reactions. This information demonstrates proper follow-up care.
Here’s a sample documentation snippet
- Administered influenza vaccine (Fluzone)
- lot #UI234A, exp 06/2024) IM in right deltoid.
- Patient consented.
- Observed for 15 minutes with no adverse reactions.
- [Provider signature]
Meeting these vaccine documentation requirements ensures compliance with CPT 90471 guidelines and reduces audit risk.
Insurance Coverage & Reimbursement
Insurance coverage for CPT Code 90471 varies by payer type.
- Medicare Part B covers preventive vaccines, including flu, pneumococcal, and hepatitis B, for at-risk beneficiaries. Medicare typically reimburses both the vaccine administration and the product separately.
- Medicaid coverage varies by state but generally includes pediatric immunizations. Most states follow the ACIP recommendations for covered vaccines. Some states also cover adult vaccines under specific conditions.
- Commercial insurance plans must cover preventive immunizations under the ACA preventive mandate.
This means most plans cover CPT 90471 when paired with appropriate preventive diagnosis codes. However, coverage details may vary between plans.
The table below shows the average 2024 CMS reimbursement rates for CPT 9047:
| Payer Type | Average Reimbursement Rate |
| Medicare Part B | $25.50 |
| Medicaid (Average) | $22.75 |
| Commercial Insurance | $28.30 |
These rates represent typical Medicare vaccine reimbursement amounts.
Actual rates may vary based on geographic location and specific payer policies. Understanding CPT 90471 Medicaid coverage in your state is essential for proper billing.
Common Billing Errors & Denial Reasons
Incorrectly documenting and coding CPT 90471 cause medical claim denials. Providers face audits, repetition of process and wastage of time.
So, avoiding mistakes while billing services and procedures under this code is crucial for faster reimbursements from insurance payors.
Here are some major mistakes, providers usually make:
Using 90471 for multiple vaccines
One common error is using 90471 for multiple vaccines instead of billing 90472 for additional injections. This mistake often leads to denials.
Missing ICD-10 Z23
Another frequent issue is the missing ICD-10 Z23. Payers typically require this diagnosis code for immunization administration claims. Without it, your claim may be rejected.
Failing to report the vaccine product code
Failing to report the vaccine product code is another common mistake. Remember that CPT 90471 only covers administration. You must also bill for the vaccine product itself.
Incomplete documentation
Incomplete documentation causes many denials. Payers may request medical records to verify services. If documentation lacks required elements, they’ll deny the claim.
The table below lists common denial codes and their solution:
| Denial Code | Reason | Solution |
| CO-16 | Claim/service lacks information | Add missing information such as ICD-10 code or modifier |
| CO-97 | The benefit for this service is included in another service | Check bundling policies and adjust billing accordingly |
| PR-204 | This service/equipment/drug is not covered | Verify coverage policies and use appropriate diagnosis codes |
Special Considerations: COVID-19 & CPT 90471
COVID-19 vaccine billing requires special attention. The administration of COVID-19 vaccines uses specific codes rather than CPT 90471. For example, Pfizer vaccine administration billing uses code 0001A or 0011A, depending on the dose.
However, CPT Code 90471 still applies in certain COVID-related scenarios. If a patient receives a COVID vaccine plus other routine immunizations, you would use the COVID-specific administration code for the COVID vaccine and CPT 90471 for other initial injectable vaccines.
Understanding 90471 COVID coding rules is essential during the pandemic. Always check the latest CMS guidelines for COVID-19 vaccine billing CPT requirements. These guidelines continue to evolve as new vaccines and dosing schedules emerge.
Compliance & Audit Risks
Vaccine billing faces significant scrutiny from oversight agencies. The OIG and CMS regularly audit immunization billing practices. These audits focus on proper coding, documentation, and medical necessity.
ICD-10 linkage accuracy with CPT Code 90471 is a common audit focus. Auditors check if diagnosis codes appropriately support the services billed. Modifier accuracy also receives close attention during reviews.
HIPAA compliance is another important consideration. Patient information related to immunizations must be protected according to privacy regulations. This includes both electronic and paper records.
To reduce compliance risks, implement regular internal audits. These reviews help identify and correct issues before external auditors find them. Training staff on vaccine billing audits and compliance requirements is essential for any practice that administers immunizations.
Tips for Providers & Billing Staff
Implementing these best practices can improve your immunization billing success.
- Create immunization billing checklists for your staff. These tools help ensure all required elements are included in each claim.
- Train staff regularly on modifiers and ICD-10 pairing. Ongoing education keeps everyone updated on coding changes and requirements. This training is especially important for new billing staff.
- Conduct regular internal audits to identify and correct issues before they result in denials. These proactive measures save time and money in the long run.
- Investing in billing staff training pays dividends through improved reimbursement rates and fewer denials.
Following these vaccine reimbursement tips can significantly improve your practice’s financial health.
Conclusion
Accurate billing for CPT Code 90471 requires attention to detail and proper documentation. This code represents a crucial service in preventive care. Proper billing ensures both compliance and optimal reimbursement.
Remember to always distinguish between vaccine administration and product codes. Use appropriate modifiers and diagnosis codes. Maintain thorough documentation to support your claims.
By following the guidelines, you can optimize your immunization billing process. For expert billing help, contact Medheave.
Our team specializes in medical billing and can help maximize your reimbursement while ensuring compliance.
FAQs
Does CPT Code 90471 cover the vaccine itself?
No, CPT Code 90471 only covers the administration service. You must separately bill for the vaccine product using a specific vaccine product code. Both codes are typically needed for complete reimbursement.
Can CPT 90471 be billed with an office visit?
Yes, you can bill CPT 90471 with an office visit using Modifier 25. This indicates that the E/M service was a separate, significant service beyond the vaccine administration.
What ICD-10 codes pair with CPT 90471?
The primary ICD-10 code is Z23 (Encounter for Immunization). Other codes like W49.0XXA (for tetanus after injury) or Z20.3 (for rabies exposure) may be used depending on the clinical situation.
What is the difference between CPT 90471 and 90472?
CPT Code 90471 is for the first injectable vaccine administered during a visit. CPT 90472 is used for each additional injectable vaccine given during the same encounter.
Is CPT 90471 covered under preventive care by Insurance?
Yes, most insurance plans cover CPT 90471 under preventive care benefits due to the ACA preventive mandate. However, coverage details may vary between plans.
What are the common denial reasons for 90471?
Common denial reasons include using 90471 for multiple vaccines instead of 90472, missing ICD-10 Z23, failing to report the vaccine product code, and incomplete documentation.
Can pharmacies bill CPT 90471 directly?
Yes, pharmacies can bill CPT 90471 directly if they have the appropriate credentials and billing systems in place. Many pharmacies now provide immunization services and bill insurance directly for these services.