Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is an essential diagnostic method for heart disease, including valves, volume loads, and heart failure. In order to properly code and charge for these procedures, healthcare practitioners are confronted with multiple codes set by the CPT, each referring to distinct features of the echocardiographic examination.
In this blog, we list and describe the most commonly reported CPT codes for TTE billing, detail the differences between them, and include Medicare coverage of Echocardiography.
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is an ultrasound-based diagnostic technique that provides real-time visualization of the heart function. An ultrasound transducer is then applied on the front of the chest to produce high-frequency sound waves that rebound off the heart and provide images of its chambers and valves as well as blood vessels. TTE helps to measure the cardiac output, determine the presence of congenital malformations, and identify such diseases as ventricular diseases, cardiomyopathies, and others. It is often applied in identifying cardiovascular diseases, assessing the state of the disease, and making therapeutic choices.
For transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), the following CPT codes are commonly used:
CPT Code 93306
- Description: Real-time routine transducer echocardiogram, transthoracically recorded with image-audio documentation incorporating both spectral and color doppler imaging.
- Usage: It remains the single most extensive code for TTE that incorporates anatomical imaging and Doppler studies. The most common reason is when a complete review of the heart is carried out, such as physical and mechanical attributes of the heart.
CPT Code 93307
- Description: Echo, transthoracic, real-time, intermittent imaging, no Doppler.
- Usage: This code refers to imaging of the structure and function of the heart without providing a Doppler analysis. It comprises fundamental imaging to evaluate heart volume, cavities, and movement of myocardium.
CPT Code 93308
- Description: Follow-up or limited study, transthoracic echocardiography.
- Usage: This code is billed for a basic or follow-up echocardiography where the scope of examination is less than when evaluating all aspects of the heart.
Add-on Codes: CPT Codes 93320, 93321, and 93325
- 93320: Discrete Doppler with pulsed wave and/or continuous wave displayed by echocardiography.
- 93321: Doppler echocardiography, pulsed wave and/or continuous wave with spectral display; follow-up or limited study.
- 93325: Sound wave analysis, color flow mapping.
- Usage: These add-on codes are appended to primary TTE codes to report when Doppler studies, spectral as well as color, are carried out to obtain more information about the blood flow through the heart and the valves.
These codes help accurately represent the type of echocardiography performed, ensuring proper billing and reimbursement.
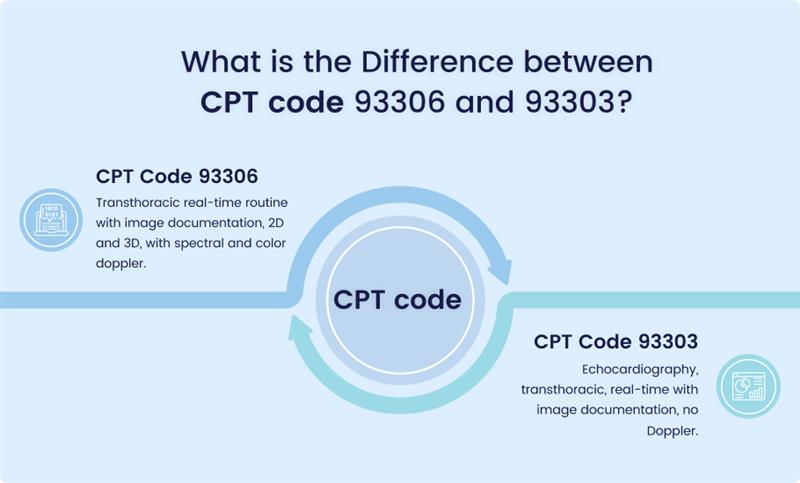
One must understand that both CPT codes 93306 and 93303 relate to transthoracic echocardiography, more commonly referred to as TTE. However, it’s important to note that these two codes involve differences in terms of degree of service and kind of echocardiographic study. Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
CPT Code 93306
- Description: Transthoracic real-time routine with image documentation, 2D and 3D, with spectral and color doppler.
- Scope: This refers to a morphological and functional assessment of the heart whereby structural images of it are obtained and Doppler analysis is done both by spectral and color Doppler analyses. A stress test helps to get a large amount of information on the condition and structure of the heart.
- Usage: Usually charged when a complete examination of the heart is made, as in evaluating the heart chambers, heart valves, or blood circulation.
CPT Code 93303
- Description: Echocardiography, transthoracic, real-time with image documentation, no Doppler.
- Scope: This code is for an echocardiography study that involves only the anatomical assessment of the heart without acquiring any Doppler information.
- Usage: It is used when an initial determination of the heart shape is necessary but a detailed blood flow analysis is not required, which is characteristic of Doppler studies.
What is the Difference between CPT Code 93350 and 93351?
Both the CPT codes 93350 and 93351 relate to echocardiography services, but they differ in procedures as well as components of the echocardiographic study. Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
CPT Code 93350
- Description:Real-time, transthoracic, image documented, echo with/or without Doppler and/or color flow mapping; interpretation and report.
- Scope: This code is for the comprehensive echocardiography, which includes real-time and Doppler studies, spectral as well as color. It is often used for data acquisition for a complete analysis that concerns the structure of the heart and the integrated function of the cardiac chambers.
- Usage: This code is often used to bill a complete echocardiogram that includes a specific, detailed evaluation of the heart chamber’s shape and function.
CPT Code 93351
- Description: Real-time two-dimensional echocardiography with image documentation, including Doppler echocardiography and/or color flow mapping if performed; follow-up/limited study with interpretation and report.
- Scope: This code is for an additional, follow-up, or limited echocardiographic study, which also entails Doppler examinations. It is utilized when a full cardiac evaluation is not required and an echocardiogram is performed for some specific aspect of the heart.
- Usage: This code may be billed when there has to be a focus on an already present condition or when there has to be a limited assessment based on previous findings.
In general, Medicare offers reimbursement for echocardiography with certain limitations, mainly when it is required for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes in cases of certain cardiovascular diseases. Here’s an overview of Medicare coverage for echocardiography:
Types of Echocardiography Covered
- Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): Medicare reimburses TTE for assessing the multiple cardiology conditions, such as heart failure, valvulopathies, and other structural heart diseases.
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): This procedure is also reimbursable when medically appropriate and tends to be used if adequate information cannot be obtained from a TTE.
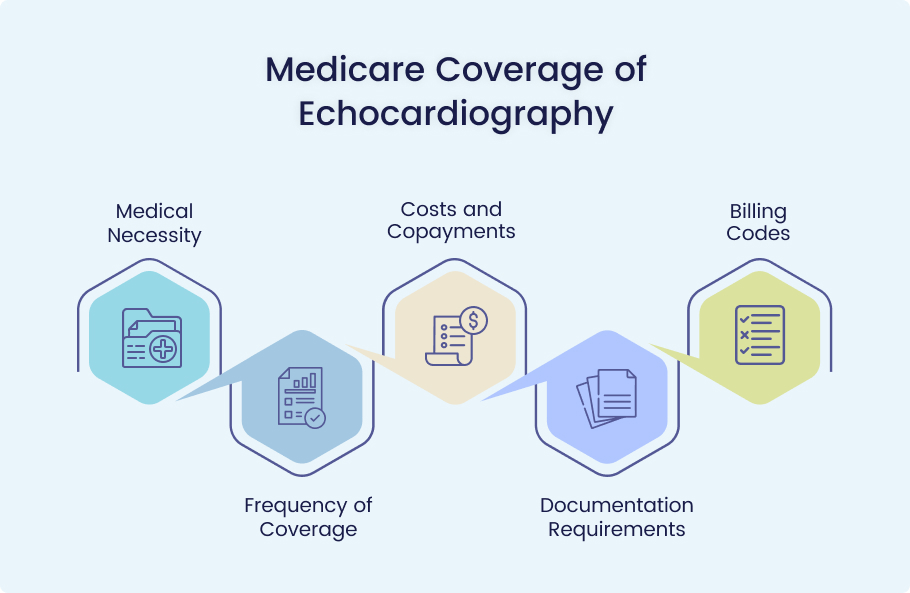
Medical Necessity
- An echocardiogram cannot be covered unless it is determined to be medically necessary. This generally comprises documents that provide justification for the test in relation to the patient’s signs and symptoms, past medical history, or results of prior tests.
- Common indications for coverage may include:
- Generally, evaluation of unexplained heart murmurs.
- Evaluation of signs and symptoms observed in heart failure (for example, dyspnea, fatigue).
- Congenital heart disease diagnosis.
- Assessment of valvular heart disease.
- Evaluation of myocardial disease, for instance, cardiomyopathy.
Frequency of Coverage
- Medicare does not restrict the number of times that echocardiography can be performed in a given year, provided there is a medical reason for the procedure to be done. However, anytime individuals request to take the test more than once, or they take the test quite often, they need to show why they need to do so.
Costs and Copayments
- Medicare Part B bases its payment on the approved amount and, in general, pays 80% of this amount after the annual deductible has been reached for echocardiography. Patients are expected to contribute the rest 20%, as it may depend on certain provisions of the health plan.
- Patients will also have to pay extra charges if the procedure will be done in a facility or hospital.
Documentation Requirements
- In order to pass coverage, the providers need to have proper documentation justifying the medical necessity of the echocardiography. This includes:
- The records that the referring physician made during the preliminary consultation.
- Any abnormal physical examination made during the physical assessment check.
- Evidence of the echocardiography that was performed is in a detailed methodological description.
Billing Codes
- It is important to bill Medicare for the appropriate CPT codes, such as 93306 for comprehensive TTE, and to include the proper ICD-10 codes that show the medical necessity for the service.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TTE is one of the most important diagnostic methods in which a variety of information about the structure and function of the heart is obtained. It is important for healthcare providers to first understand the various CPT codes like 93306, 93303, 93350, and 93351 to support right billing and reimbursement for such services. Documentation of medical necessity, especially on the clinical signs and specifications, also helps substantiate the correct coding and eligibility of Medicare and other insurance providers. With these guidelines, the providers get to improve patient care while covering its billing issues. Since echocardiography remains an essential tool in managing cardiovascular diseases, understanding coding and billing trends will help patients get proper diagnostic examinations promptly.
For comprehensive insights into our medical coding services, visit the Medheave website today!