Inpatient rehabilitation facilities offer essential services that include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech-language pathology, etc. At the heart of this process is CPT coding, which plays a crucial role in translating the wide array of rehabilitation services into billable units . However, the process is not without any glitches. Rehabilitation billing requires extra precision, coding knowledge, and even payer-specific information.
In this blog, we will discuss the different CPT codes applicable for inpatient rehabilitation, the problem areas that are likely to be faced, and how best to address them.
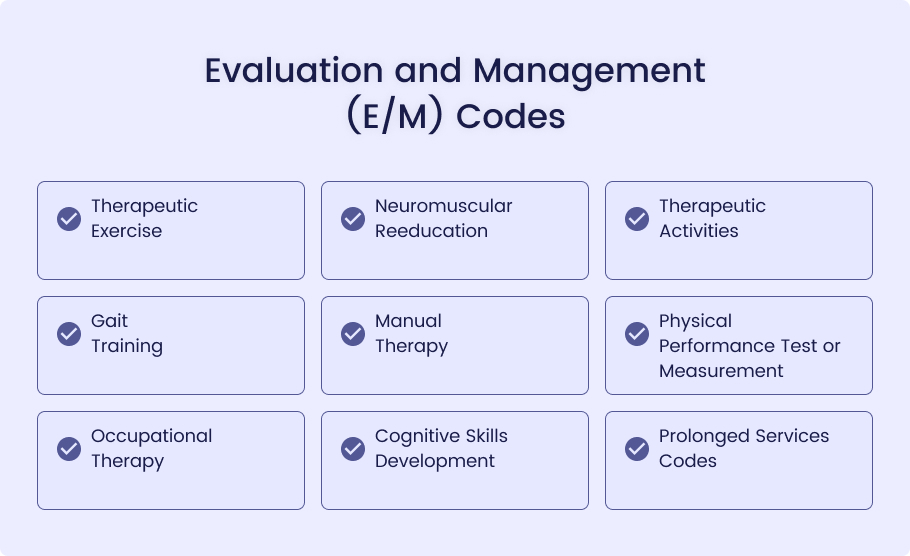
Rehabilitation as a category of inpatient care uses a unique set of numerical codes known as CPT codes for medical, therapeutic, or diagnostic services delivered to rehabilitated patients. These codes are from the current procedural terminology system that aids the documentation and billing, making it easier to get appropriate reimbursement. In the inpatient rehab settings, CPT codes encompass a wide variety of services like initial medical exams (e.g., 99221-99223), therapeutic exercises (e.g., 97110), neuromuscular re-education (e.g., 97112), and the like.
Inpatient rehabilitation entails various services that require unique CPT codes for accurate billing and documentation purposes. Here are some key CPT codes commonly employed during inpatient rehabilitation:
99221-99223: These codes are utilized in the initial evaluation and management of patients admitted to an inpatient rehabilitation facility, depending on the complexity of medical decision-making as well as history gathering and examinations conducted.
Therapeutic Exercise
97110: This code is intended for neuromuscular reeducation of movement, balance, coordination, kinesthetic sense posture, and proprioception in sitting and standing activities.
Neuromuscular Reeducation
97112: This code encompasses dynamic exercises designed to increase functional performance, such as lifting, bending, or carrying. Sessions of 15 minutes duration are charged accordingly.
Therapeutic Activities
97530: This code refers to gait training therapy, which includes helping patients learn to walk again or improve their walking ability through specific therapeutic activities.
Gait Training
97116: This code is used for gait training therapy, which includes helping patients learn to walk again or improve their walking ability through specific therapeutic activities.
Manual Therapy
97140: This code refers to techniques employed in manual therapy such as mobilization and manipulation of muscles and joints in order to improve function and alleviate pain.
Physical Performance Test or Measurement
97750: This code is used for the testing of physical performance with a report analyzing the results. This can include tests of strength, balance, coordination, or functional capacity.
Occupational Therapy
97535: This code encompasses self-care/home management training for people living independently, such as activities of daily living (ADL) training and compensatory strategies, meal preparation, safety procedures, and providing instruction in using assistive technology devices.
Cognitive Skills Development
97129-97130: These codes are utilized for cognitive function interventions that aim to strengthen attention, memory, problem-solving, and other cognitive skills. The initial 15-minute session should be billed with code 97129, while any subsequent 15-minute sessions can use code 97130.
Prolonged Services Codes
99354-99355: When rehabilitation services extend beyond their usual duration, additional billing can occur based on this additional time spent.
These codes are essential for capturing the full scope of services provided in inpatient rehabilitation, ensuring that facilities are reimbursed appropriately for the care they deliver.
Here is a table summarizing the key CPT codes for inpatient rehabilitation:
| Service Category | CPT codes | Description |
| Evaluation and Management (E/M) | 99221-99223 | Initial evaluation and management of patients admitted to an inpatient rehab facility. |
| Therapeutic Exercise | 97110 | Exercise to develop strength, endurance, range of motion, and flexibility (per 15 minutes). |
| Neuromuscular Reeducation | 97112 | Reeducation of movement, balance, coordination, posture, and proprioception. |
| Therapeutic Activities | 97530 | Dynamic activities to improve functional performance (per 15 minutes). |
| Gait Training | 97116 | Gait training therapy to improve walking ability. |
| Manual Therapy | 97140 | Manual therapy techniques, including mobilization and manipulation of muscles and joints. |
| Physical Performance Test | 97750 | Testing of physical performance with an analysis report (e.g., strength, balance). |
| Occupational Therapy | 97535 | Self-care/home management training, including ADL and compensatory training. |
| Cognitive Skills Development | 97129-97130 | Cognitive function interventions to improve attention, memory, and problem-solving (per 15 minutes). |
| Prolonged Services | 99354-99355 | Additional billing for rehabilitation services that extend beyond typical time. |
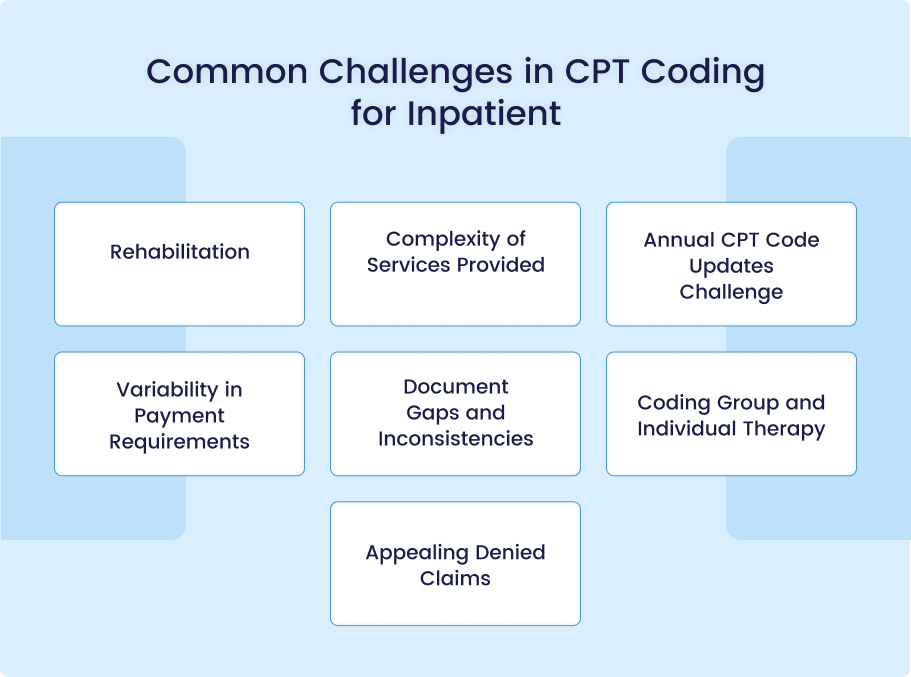
CPT coding for inpatient rehabilitation presents unique obstacles that can complicate billing processes, possibly leading to delays or denials of payments or reimbursements. Recognizing these issues is crucial in order for rehabilitation facilities to maintain accurate and compliant billing practices; here are some of the more frequent ones:
Complexity of Services Provided
Challenge: A key challenge associated with inpatient rehabilitation services is navigating its wide array of services, which range from physical therapy to cognitive skills development and require specific CPT codes for documentation and coding purposes. Accurate documentation of and coding these varied services can often result in errors being missed during billing processes.
Impact: Misunderstanding or overlooking appropriate CPT codes can result in under-coding or over-coding, leading to reduced potential revenue or increasing risk for audits and penalties.
Solution: Training staff on all services and their corresponding CPT codes is key for optimal service delivery, while using software with automated checks can further minimize errors.
Annual CPT Code Updates Challenge
Challenge: The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code set is annually revised to account for changes in medical practice, technology, and services. Rehabilitation facilities need to keep abreast of these developments, but this can prove challenging when staff are not quickly informed or trained on them.
Impact: Failing to use up-to-date codes may lead to claim rejections or denials by payers who do not recognize these outdated codes.
Solution: Implement a program of staff education regarding CPT code updates through regular online training sessions, workshops, or newsletters. Also, make sure your billing software stays up-to-date with the newest CPT codes.
Variability in Payment Requirements
Challenge: Different payers have differing requirements on how CPT codes should be utilized, documented, and billed; this variation can prove especially challenging when treating multiple payers for one patient at once.
Impact: Uneven application of payer-specific rules can result in denied claims, delayed payments, and an increased administrative burden in resubmitting claims.
Solution: Create and regularly update a payer-specific billing guide that outlines their requirements, then train staff on how to adhere to it when submitting claims. Furthermore, consider billing software with customizable features to meet each payer’s specifications.
Document Gaps and Inconsistencies
Challenge: Lack of Documentation An incomplete or inconsistent documentation system can be an impediment to inpatient rehabilitation services, leading to claim denials due to difficulty justifying services billed for. Any gaps can make justifying billable services harder and potentially lead to claims being denied by insurance providers.
Impact: Poor documentation can result in lost revenue due to denials, audits, or penalties for noncompliance.
Solution: Establish strict documentation protocols with detailed records for every service provided. Use standard forms and templates for consistency, and perform regular audits of patient records to detect any documentation issues before claims are filed.
Coding Group and Individual Therapy
Challenge: Rehabilitation programs often combine both individual and group therapy sessions, making coding for them complex. Incorporating all appropriate CPT codes, which vary greatly between these different therapy formats, is crucial to effective care delivery.
Impact: Misidentifying therapy sessions or using incorrect CPT codes can result in billing mistakes, leading to denied claims or reduced reimbursements.
Solution: Ensure staff members understand the distinctions between individual and group therapy codes. Implement clear protocols for documenting each type of therapy session, and utilize software that distinguishes these services when creating claims.
Appealing Denied Claims
Challenge: Unfortunately, claim denials are an often-experienced part of rehabilitation billing. Successfully appealing them requires having in-depth knowledge of why these claims have been denied and being able to provide enough documentation that supports services billed.
Impact: Failing to effectively appeal denied claims can result in lost revenue and higher administrative costs, both of which can reduce efficiency.
Solution: Implement an efficient process for reviewing denied claims, understanding why they have been rejected, and collecting the necessary documentation for appeals. Educate staff in effective appeal strategies while monitoring outcomes to increase success rates in future appeals.
Conclusion
Mastering CPT coding for inpatient rehabilitation is key to accurate billing and receiving appropriate reimbursements, yet its complexity can be daunting. As healthcare facilities strive to manage diverse services while adhering to ever-evolving coding rules and payer requirements, their facilities face considerable financial strain if these challenges aren’t tackled effectively. Implementing best practices can reduce risks, but for facilities looking for an easier route, outsourcing to MedHeave Medical Billing Services could be the way forward. MedHeave’s Medical billing services expertise in rehabilitation billing allows your facility to reduce errors, maximize revenue growth, and focus more on providing quality patient care with ease.