In medical billing, a CO-16 denial happens when a payer rejects a claim due to missing, inaccurate, or incomplete information. It is one of the most common reasons for refusal and usually results from minor data entry or documentation errors that delay processing.
CO-16 falls under Contractual Obligation (CO), so providers cannot bill the patient for the denied amount. According to CMS and most payers, code 16 means the claim “lacks information or has submission or billing errors.”
CO-16 denials often occur when key claim details—such as patient information, CPT or ICD-10 codes, provider NPIs, or insurance data—are missing or inaccurate.
Remark codes on the Explanation of Benefits (EOB)—such as M51 (incorrect procedure), N290 (invalid provider ID), or MA63 (missing date of birth)—help billing teams identify issues, correct them, and resubmit claims.
This blog covers common causes of CO-16 denials, explains how to fix them, and shares best practices to prevent them, helping protect your revenue cycle.
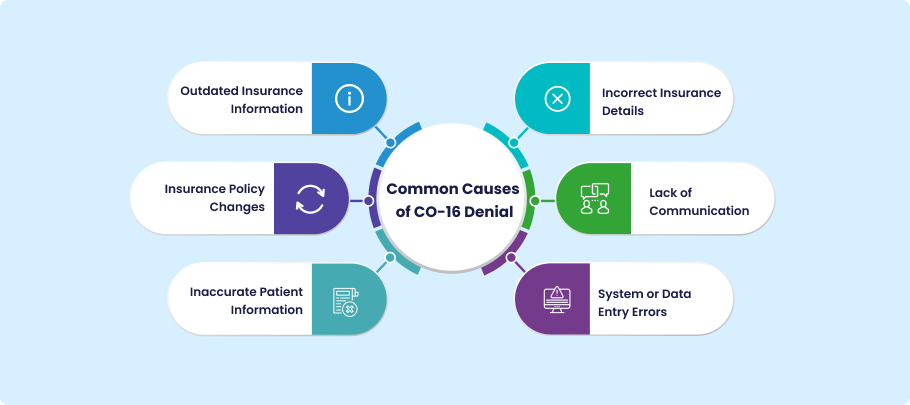
Common Causes of CO-16 Denial
The CO-16 denial code usually results from preventable errors in data accuracy or claim submission. Even minor mistakes in patient or insurance information can lead to delayed or denied reimbursements. Understanding these common causes helps billing staff identify the source of the problem and take quick corrective action.
Outdated Insurance Information
Using outdated insurance information is one of the most common causes of CO-16 denials. Patients often change jobs or insurance providers, but their EHR or billing system records are not always updated. Claims submitted with expired coverage, outdated plan details, or inactive policy numbers are automatically rejected.
Incorrect Insurance Details
Inaccurate payer information—like a wrong member ID, plan code, or payer address—can make a claim incomplete or invalid, even if coverage is active. These errors often happen during manual data entry or patient registration. This highlights the need for careful pre-submission verification to ensure accurate billing.
Insurance Policy Changes
Unexpected updates to payer policy guidelines or plan structures can affect how claims must be submitted. If the billing system is not aligned with the payer’s latest requirements, updates to required fields, coding rules, or claim formats may lead to denials. Staying current with these changes requires consistent communication with payers.
Lack of Communication
Missing claim information can also result from poor communication between clinical, billing, and front-desk teams. For instance, payers may flag clinical documentation if it doesn’t match billing records. Clear workflows and regular internal audits help prevent these errors.
Inaccurate Patient Information
Claim mismatches often occur due to incorrect or missing patient information, such as name spelling, birthdate, gender, or address. Although these minor errors commonly cause CO-16 denials, they can be easily prevented with regular data verification.
System or Data Entry Errors
Technical glitches or human mistakes can cause duplicate claims, wrong codes, or missing fields. You can prevent many of these errors by keeping systems accurate, training staff on claim entry rules, and running automated checks before submission.
Impact of CO-16 Denials on Revenue Cycle
Although it may seem like a simple data error, the CO-16 denial code can have a significant impact on the revenue cycle. Each denial disrupts cash flow that supports operations and patient care, delays reimbursement, and increases administrative workload. Frequent denials create backlogs that slow overall claim performance and reduce collection efficiency.
How CO-16 Affects Claim Turnaround
A single CO-16 denial can extend claim turnaround times by days or even weeks. While waiting for the payer to reprocess a claim, billers must locate any missing information, correct it, and resubmit the claim. Payment delays increase the time spent fixing errors and disrupt the provider’s cash flow.
Examples of Delays or Payment Losses Due to CO-16
A missing birthdate or incorrect provider NPI may seem minor, but the claim cannot proceed until these issues are resolved. Even a few CO-16 denials can delay thousands of dollars in payments for large practices or hospitals. These delays also raise administrative costs, as staff spend more time correcting avoidable errors.
Why Co-16 Is Common in Multi-payer Billing Environments
In multi-payer billing, each payer has its own rules for claim submission. What one payer accepts, another may reject. These differences increase errors, making thorough pre-submission checks essential. Misalignment with payer rules can quickly result in CO-16 denials, which can impact revenue and workflow.
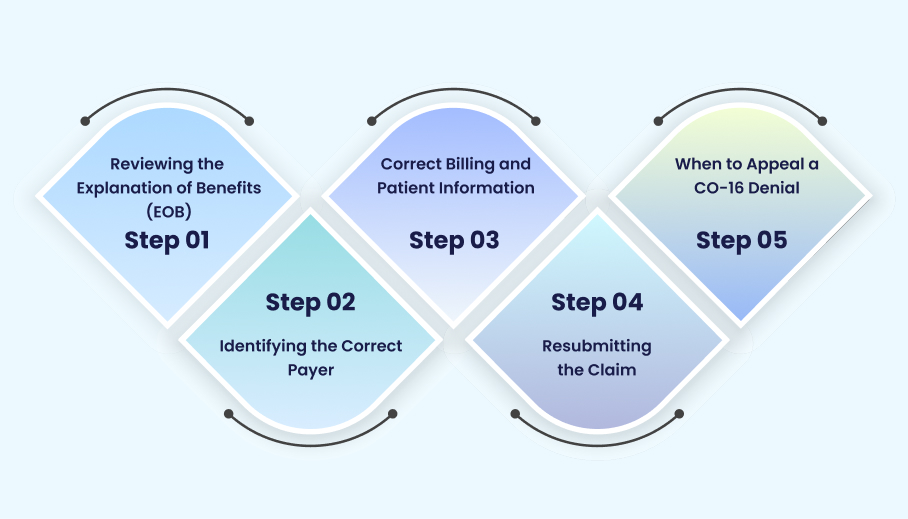
How to Fix a CO-16 Denial
A straightforward, step-by-step approach helps identify errors, fix them, and get claims approved, resolving CO-16 denials. Handling denials properly not only speeds up reimbursement but also reduces the likelihood of repeated errors and administrative work.
Reviewing the Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
The first step is to review the EOB or ERA carefully. These documents display the exact remark codes and reasons for denial—codes such as M51 (invalid procedure) or N290 (incorrect provider ID) pinpoint the issue. A thorough review lets billers focus on the correct fix without guessing.
Identifying the Correct Payer
A CO-16 denial may occasionally happen because the claim was submitted to an out-of-date plan or the incorrect payer. Verify the current payer information to ensure the correct insurance company is receiving the claim. Double-checking eligibility and coverage details can help avoid rejection before resubmission.
Correct Billing and Patient Information
Next, update the claim with accurate patient and billing data. CPT/ICD-10 codes, patient demographics, NPI numbers, and insurance policy details may all require updates. The likelihood of recurring CO-16 denials can be reduced by using automated claim scrubbers or pre-submission verification tools to identify and correct these errors before resubmitting.
Resubmitting the Claim
Resubmit the claim as soon as the necessary modifications are made. To prevent any delays, provide any supporting paperwork that the payer requests.Track the resubmission to ensure the claim is processed promptly and payment is received without further delay.
When to Appeal a CO-16 Denial
Sometimes, even with correct information, the payer may reject the claim because of a misunderstanding or a malfunctioning system. Consider filing an appeal if the denial persists after correction. Provide thorough documentation, concise justifications for the changes made, and any EOB references to bolster your argument. A previously rejected CO-16 claim may be successfully paid with a well-organized appeal.
Strategies to Prevent CO-16 Denials
It is always more effective to prevent CO-16 denials than to correct them afterward. By taking proactive measures, healthcare providers can maintain a healthier revenue cycle, reduce administrative workload, and improve claim accuracy.
Ensuring Accurate Patient Registration
Accurate patient registration is key to preventing CO-16 denials. Collect and confirm all patient information at registration, including name, date of birth, contact details, and insurance numbers. Verifying this information twice lowers the risk of claim rejections due to errors or missing data.
Verify Insurance Coverage Before Service
Before providing services, always check a patient’s coverage and benefits. Pre-submission verification of eligibility, plan status, and payer requirements ensures cleaner, more accurate claims and reduces first-pass denials. This reduces CO-16 denials caused by incorrect or outdated insurance information.
Conducting Regular Billing Audits
Regular billing audits can identify common claim errors, such as incorrect provider details or incorrect CPT/ICD codes. Catching and correcting these mistakes early helps staff improve claim quality and reduces the likelihood of repeated denials.
Training Staff on Verification Protocols
Staff training is essential to ensure that everyone is familiar with verification procedures, documentation guidelines, and claim submission requirements. Well-trained staff are less likely to make data errors and can spot issues before claims are sent to the payer.
Using Technology for Eligibility Checks (EHR & Billing Software)
Many verification tasks can be automated with EHR and billing software. These tools automatically check eligibility and scrub claims. Automation reduces human errors. It also helps claims get accepted the first time by finding missing information, checking payer rules, and confirming patient details.
Using these strategies, providers can reduce CO-16 denials, expedite claim processing, and safeguard their revenue.
CO-16 vs. Similar Denial Codes
CO-16 is different from other denial codes. Knowing this helps billing teams identify the problem quickly and resolve it. CO-16 typically occurs when claim data is missing or incorrect. Other codes occur for reasons such as incorrect provider information or payer mismatches.
| Denial Code | Description | Key Difference |
| CO-16 | Claim/service lacks necessary information | Denial occurs due to missing or incorrect claim data |
| CO-109 | Sent to the wrong payer | Denial relates to payer mismatch, not missing data |
| CO-197 | Provider not credentialed | Denial occurs due to a provider eligibility issue |
By comparing these codes, providers can avoid unnecessary resubmissions and follow the right fix. CO-16 means correcting claim data, CO-109 may require sending the claim to the correct payer, and CO-197 involves checking provider credentials before submission.
Example Scenario of a CO-16 Denial
Consider the following actual situation from a regular outpatient clinic to gain a deeper understanding of a CO-16 denial.
Real-World Case Example
A clinic filed a claim for a patient’s standard diagnostic test. On the EOB, the claim was first rejected with a CO-16 denial code. The EOB indicated that the patient’s date of birth was missing from the claim submission.
What Went Wrong
When registering the patient, the front desk employees unintentionally left the date of birth field empty. The payer marked the claim as incomplete even though the insurance information and procedure codes were accurate. This illustrates how a minor mistake can lead to the denial of a CO-16 claim.
How it was Resolved
After reviewing the EOB and identifying the missing information, the billing team updated the patient’s record in the system. After making corrections, they resubmitted the claim to the payer. The clinic was quickly reimbursed after the claim was satisfactorily handled. This case underscores the importance of accurate patient data, thorough pre-submission verification, and prompt resolution of CO-16 denials.
Best Practices for Denial Prevention
Technology, process enhancements, and staff collaboration are all necessary to prevent CO-16 denials and other typical claim rejections. Using best practices safeguards your revenue cycle and maintains claim accuracy.
Integrating Claim Scrubbing Software
Missing or inaccurate data can be automatically detected using claim-scrubbing tools before submission. By verifying insurance information, procedure codes, and patient demographics, these systems lessen the possibility of CO-16 and other medical billing denial codes.
Automating Eligibility Verification
Automating eligibility checks ensures that patient coverage and benefits are verified before services. This proactive step reduces errors from outdated or incorrect insurance and improves first-pass claim acceptance rates.
Improving Communication Between Front Desk and Billing Teams
Clinical, billing, and registration teams must communicate clearly. Sharing updated patient and insurance information quickly prevents claim discrepancies. Regular meetings and clear procedures build accountability and reduce CO-16 denials.
Consistently applying these practices helps providers reduce common denials, streamline revenue cycle management, and enhance financial performance.
Final Recommendations
A proactive and well-organized billing process is the first step in preventing CO-16 denials. Even though these denials frequently result from straightforward mistakes, regular attention to claim accuracy can significantly lessen their impact and frequency.
Automate Claim Validation
Utilize automated techniques to verify claims before submission. Claim scrubbers assist in guaranteeing that every claim satisfies payer standards on the first attempt by promptly identifying missing data, erroneous codes, or format problems.
Maintain Updated Payer Records
Ensure your plan details and payer database are up to date. Outdated records may result in needless CO-16 denials because payer regulations, policies, and electronic submission formats are constantly changing. Maintain compliance by routinely reviewing payer correspondence.
Review Denial Trends Regularly
Monitor and review denial trends in your billing system to find areas for improvement. Tracking CO-16 and related denials helps uncover the root causes, such as system issues, documentation gaps, or registration errors.
Educate Billing Staff
Ongoing staff training is essential. Teach coding, billing, and front-desk teams about payer rules, proper verification, and best practices for accurate claim entry. A well-informed team is the best defense against denials.
Following these steps helps healthcare organizations maintain cleaner claims, expedite reimbursements, and enhance revenue cycle efficiency.
Conclusion
CO-16 denials are common in medical billing, but they can be prevented. Providers can reduce denials and improve claim success by verifying information upfront, utilizing the right technology, and regularly training their staff. Automating eligibility checks, maintaining up-to-date patient and payer records, and promoting clear communication between teams help ensure cleaner claims and faster reimbursements.
Medheave medical billing services help healthcare organizations prevent CO-16 and other avoidable denials. We combine advanced verification tools with expert claim analysis to make sure every claim meets payer requirements the first time. Partner with Medheave to streamline your revenue cycle, stay compliant, and expedite billing.
FAQs
Q1: What does CO-16 denial mean in medical billing?
CO-16 is a denial code indicating that a claim was rejected due to missing, incorrect, or incomplete information. It often results from small data entry or documentation errors.
Q2: How can I fix a CO-16 denial?
To fix a CO-16 denial, review the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) for the specific error, correct the inaccurate or missing information (like patient details, CPT/ICD codes, or provider NPI), and resubmit the claim.
Q3: What are common causes of CO-16?
CO-16 denials commonly occur due to incorrect patient demographics, incorrect CPT or ICD-10 codes, invalid provider information, missing insurance data, or discrepancies between clinical and billing records.
Q4: Is CO-16 the same as CO-109?
No. CO-16 refers to claims with missing or incorrect information, while CO-109 generally involves redirecting the claim to the correct payer. Each code requires a different approach to resolution.
Q5: How can billing software prevent CO-16 errors?
Billing software can prevent CO-16 denials by automating eligibility checks, validating patient and payer information, flagging missing or incorrect data, and guiding staff with built-in claim-scrubbing tools.